What Is the Most Reliable Form of Assessment? A Comprehensive Guide to Evaluating Learning Effectiveness: Are you tired of unreliable assessments that leave you guessing about your true abilities? Well, fret no more! In this blog post, we will unravel the mystery and unveil the most reliable form of assessment. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or simply curious about the inner workings of evaluation methods, we’ve got you covered. Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of assessment reliability and discover the key to accurate and meaningful evaluations. So, buckle up and prepare to be amazed by the power of reliable assessment methods!
Understanding the Reliability of Assessment Methods
When it comes to evaluating student understanding and performance, educators and trainers rely on a variety of assessment methods. However, not all assessments are created equal. The reliability of an assessment method is a crucial factor that educators must consider. Reliability, by definition, refers to whether an assessment instrument gives consistent results across multiple administrations under the same conditions with the same subjects. This consistency is the cornerstone of any effective assessment strategy.
Multiple Choice and Selected Response Items
Multiple choice tests and selected response assessments are among the most reliable forms of assessment, as they provide clear, quantifiable markers for student performance. The structured nature of these assessments limits the scope for interpretation when scoring, ensuring that results are objective and consistent. This standardization is key to their high reliability, as it minimizes the risk of subjective grading influencing the outcomes.
Constructed Responses and Open-ended Assessments
In contrast to multiple choice tests, constructed responses and other open-ended assessments such as essays and performance tasks involve a greater degree of scorer interpretation. Although these types of assessments can offer a deeper insight into a student’s understanding and abilities, they tend to have lower reliability due to the subjective nature of the grading process. This can lead to variability in results, which may not truly reflect a student’s competency or knowledge.
The Power of Formative Assessment
Despite the reliability concerns with certain open-ended assessments, formative assessment stands out as the most influential type for enhancing student learning. Formative assessment is an ongoing process that involves regular, interactive checks of student progress and understanding during the learning journey. It’s not just about measuring what students have learned; it’s about actively shaping the learning process as it unfolds.
Examples of Formative Assessments
- Quick quizzes
- In-class discussions
- Peer reviews
- Interactive activities
- Progress tracking portals
Through these activities, educators can gather real-time insights into student performance and tailor instruction to better meet individual needs. The dynamic and adaptive nature of formative assessment makes it a highly effective tool for promoting understanding and improving performance.
Direct Assessment for Specific Learning Goals
Direct assessment is designed to measure specific learning outcomes, objectives, or goals. It is the most effective form of assessment when you have a clear, singular focus. Examples of direct assessments include standardized tests, practical exams, and project-based evaluations, all of which aim to directly measure a student’s proficiency in a particular area.
Advantages of Direct Assessment
- Clarity in objectives
- Measurable outcomes
- Objective scoring methods
By concentrating on particular learning targets, direct assessments provide clear evidence of student achievement and proficiency. This is invaluable for educators seeking to understand how well their students are meeting specific standards or objectives.
Authentic Assessment: Bridging Real-world Relevance
Authentic assessment is another key player in the realm of educational evaluations. It is considered the most genuine method because it asks students to apply their skills and knowledge in contexts that closely resemble real-world situations. These assessments often take the form of case studies, internships, and projects that require the application of learned concepts in practical environments.
Why Authentic Assessment Matters
- Encourages higher-order thinking skills
- Aligns with real-world challenges
- Provides a holistic view of student abilities
Although authentic assessment may face challenges in terms of reliability due to the complexity and variability of real-world tasks, its value lies in preparing students for the practical application of their knowledge beyond the classroom.
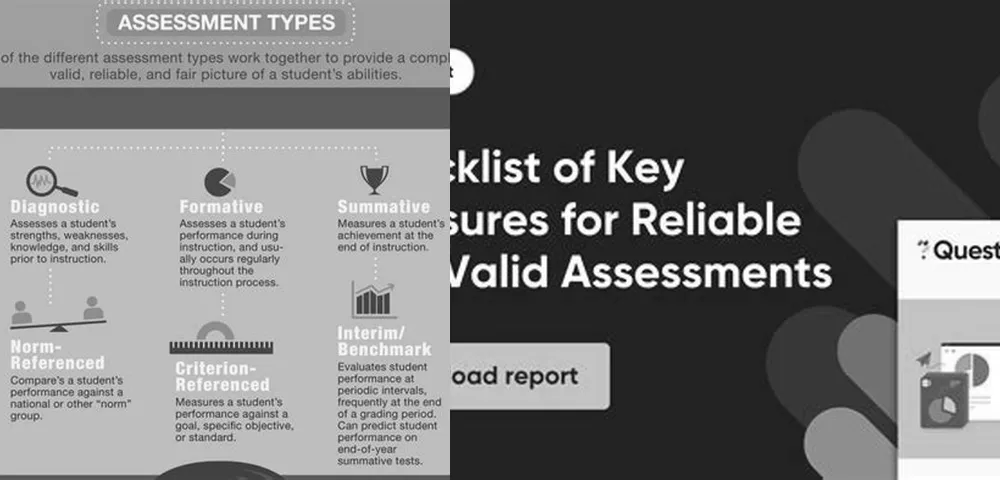
The Role of Diagnostic Assessment in Learning
Diagnostic assessment is a preemptive evaluation method that identifies a learner’s strengths, weaknesses, and prior knowledge before instruction begins. By understanding where students are starting from, educators can tailor their teaching strategies to address the specific needs of their class. This type of assessment is favored for its ability to inform instructional design and to set a baseline against which future learning can be measured.
Implementing Diagnostic Assessments
Typically, diagnostic assessments involve a series of questions or tasks given at the start of a course or training session. The findings from these assessments are then used to customize the learning experience, ensuring that instruction is relevant and targeted to the learner’s current level.
Diverse Assessment Types for Comprehensive Evaluation
There is a spectrum of assessment types employed in education to capture the multifaceted nature of learning. These include:
Observation, essays, interviews, performance tasks, exhibitions, and demonstrations, portfolios, journals, and teacher-created tests.
Each of these assessment types brings a different perspective to the table, allowing educators to compile a more comprehensive picture of student learning. While some prioritize reliability, others focus on authenticity or provide detailed diagnostic information.
Conclusion: Balancing Reliability and Relevance
In summary, while multiple choice and selected response items are noted for their high reliability, other forms of assessment such as formative, direct, authentic, and diagnostic assessments offer their own unique advantages. The key for educators is to balance the need for reliable assessment results with the need for assessments that are relevant, engaging, and informative. By employing a mix of assessment types, educators can obtain a nuanced understanding of student learning and create instructional strategies that are both effective and responsive to student needs.
Ultimately, the most reliable form of assessment is one that is aligned with educational goals, is sensitive to the context of learning, and is applied thoughtfully to support student growth. Whether through structured tests or dynamic, formative methods, it’s the careful consideration of when and how to use each type of assessment that will most effectively drive learning outcomes.
FAQ & Common Questions about the Most Reliable Form of Assessment
Q: What is the most reliable form of assessment?
A: Multiple choice and selected response items and assessments tend to have higher reliability than constructed responses and other open-ended item or assessment types.
Q: What is the most effective type of assessment?
A: Formative Assessment is the most powerful type of assessment for improving student understanding and performance.
Q: What is direct assessment?
A: Direct assessment is the most effective form of assessment when measuring a single learning outcome, objective, or goal.
Q: What is reliability in assessment?
A: Reliability refers to whether an assessment instrument gives the same results each time it is administered.
Q: What are the advantages of formative and summative assessments?
A: Formative and summative assessments are popular and efficient because they are cost-efficient, take a relatively short amount of time to create and grade, and provide a numerical summary (grade) of how much a student has learned.